Ataxia is a lack of motor (muscle coordination). Ataxia is usually caused by damage to the cerebellum.
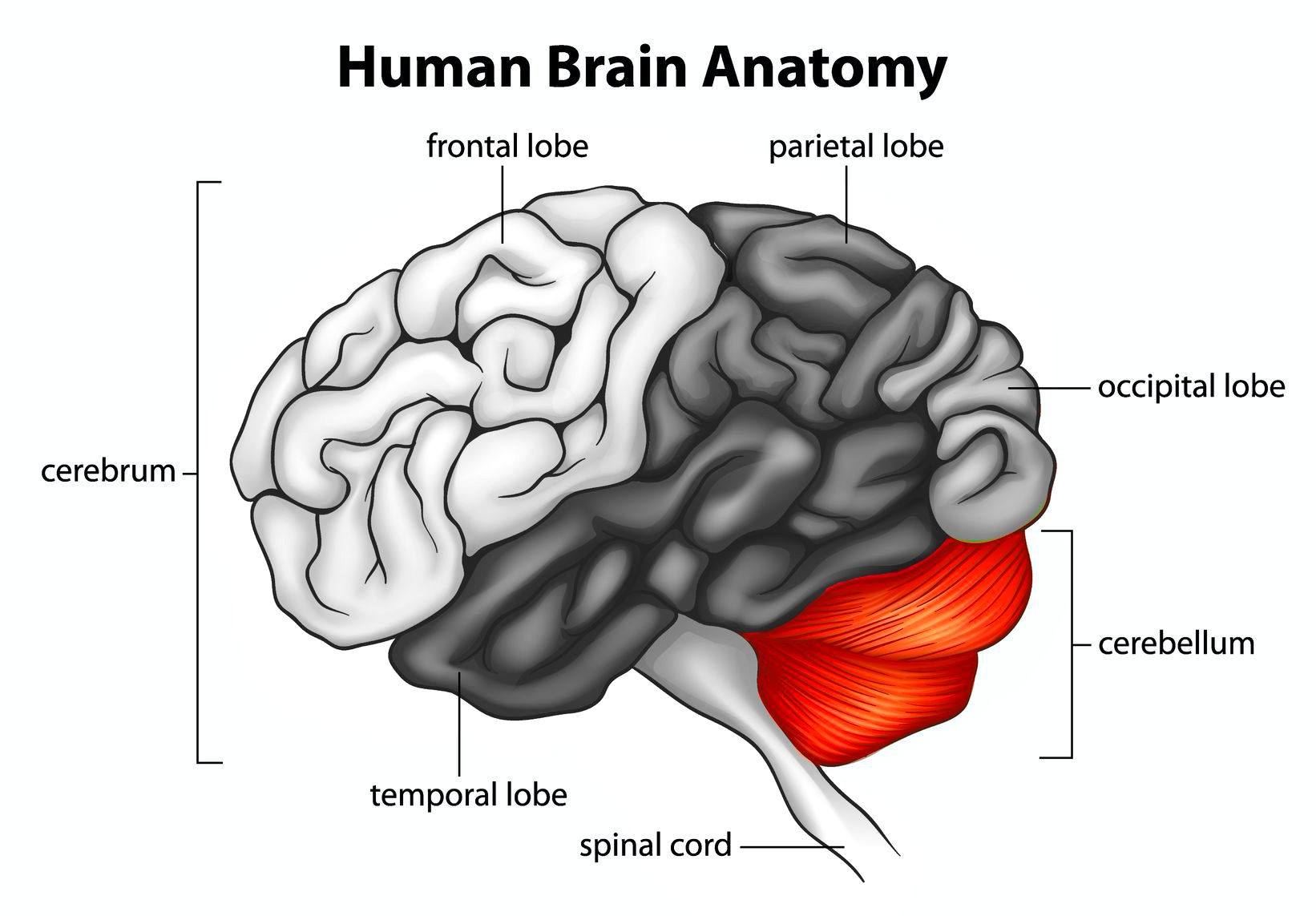
The cerebellum is located in the back of the brain and is responsible for:
- Coordinating voluntary movement of the arms and legs
- Controlling postural muscles
- Fine motor
- Eye movement
- Coordinating the muscles used for speaking
What are the types of Ataxia?
Acquired Ataxia
Damage to the brain or spinal cord can cause ataxia. This is called acquired ataxia
Hereditary Ataxia
Ataxia can also be the result of a faulty gene that causes degeneration of the brain and spinal cord. This is referred to as hereditary ataxia.
Idiopathic or Cerebellar Ataxia
Sometimes there is no known cause for ataxia. This type of ataxia is referred to as idiopathic ataxia or cerebellar ataxia
Acquired Ataxia
Acquired ataxia can have a wide range of potential causes including:
- Traumatic brain injury
- Bacterial brain infection (meningitis and/or encephalitis)
- Disruption in blood flow to the brain: stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Cerebral palsy – brain damage that occurs before, during, or shortly after birth.
- Multiple sclerosis
- Sustained long term alcohol misuse
- Underactive thyroid gland
- B12 deficiency
- Brain tumors
- Medications such as benzodiazepines
Symptoms
- Problems with coordination
- Balance problems
- Clumsiness
- Difficulty writing and/or picking up small objects
- Slurred speech
- Tremors
- Difficulty eating or swallowing
- Abnormal eye movement (nystagmus)
How is Ataxia Treated?
The treatment for ataxia will depend largely on the underlying cause. There are some medications that might help to lessen the severity of the symptoms. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can significantly help to improve movement quality and reduce the impact that the movement problems may have on your life.
Occupational Therapy (OT) – An OT will help you to improve your fine motor skills including writing, buttoning, and picking up small objects (fine motor).
Speech Therapy (ST) – A speech therapist will work on improving coordination in the “speaking muscles”, and swallowing muscles.
Physical Therapy (PT) – PT will focus on retraining the entire balance system (the cerebellum plays a MAJOR role in the balance system). A physical therapist is also skilled in retraining the “quality” of arm and leg movement. This will involved working on the “smoothness” and accuracy of the movement. For example when reaching for an object with the arm or stepping the foot forward with walking. Additionally, PT will also provide exercises to strengthen the muscle that keep the trunk steady. This is critical in providing a stable base and will assist with the quality of arm and leg movement.
Other Articles You May Be Interested In:
Walking Exercises for Stroke Patients
Many people inquire about the "best exercises" for stroke patients to improve walking. I like to use the term "Drills" when referring to "stroke exercises". Why? Because "Drills" are what I think of when I think of repetitive movement. Case and point, drills are...
Balance Training for Ataxia
Balance training is a critical component for anyone with ataxia. This is due to the fact that ataxia negatively impacts the balance system and is one of the leading causes of disability. Ataxia is caused by damage to the cerebellum. The cerebellum plays a MAJOR role...
Relearn to walk: Progression (with videos)
Are you super eager to relearn to walk? Walking is a HUGE goal for anyone who has lost that ability. Walking means different things to different people. And quite honestly, has far less meaning until you have lost this fundamental skill. All that being said, it is...
Regain Normal Walking After a Stroke: Advanced
A common goal after a stroke or a brain injury is to regain "normal walking". However, this goal is not limited to just those who have suffered a stroke. I dare say it is the number one goal of almost everyone who has suffered an injury to their neurologic system. ...
Stand and Walk After a Stroke: Intermediate Progression
Many want to stand and walk after a stroke. Of course, this is critical in giving someone more independence. However, standing and walking is also important to prevent deconditioning, maintain joint health, and prevent postural abnormalities associated with prolonged...
Product Spotlight: A step stool with handle
A step stool with a handle is one of the most seems like an odd piece of "rehab equipment", however, it is truly "worth its weight in gold". It is probably the one itemI can honestly say I use multiple times a day in my clinic. And, rarely as an actual step stool....
Gym Ball Exercise Routine for Better Balance
A Gym ball exercise routine is a great way to improve your balance. If provided with the correct exercises, they can challenge almost every "problem area" for a stroke survivor. The main areas that are problematic after a stroke are steadiness, symmetry, and dynamic...
Balance Problems After a Stroke
Balance is an even distribution of weight within a base to maintain an upright position. Balance problems are very common after a stroke. Balance is a critical part of almost all of our daily activities. Lack of balance confidence can elicit fear and anxiety. More...








