Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that affects the nerves in the brain that produce the neurotransmitter, dopamine. Parkinson’s disease primarily affects the motor system (part of the nervous system that controls body movement.
Parkinson’s Disease Anatomy
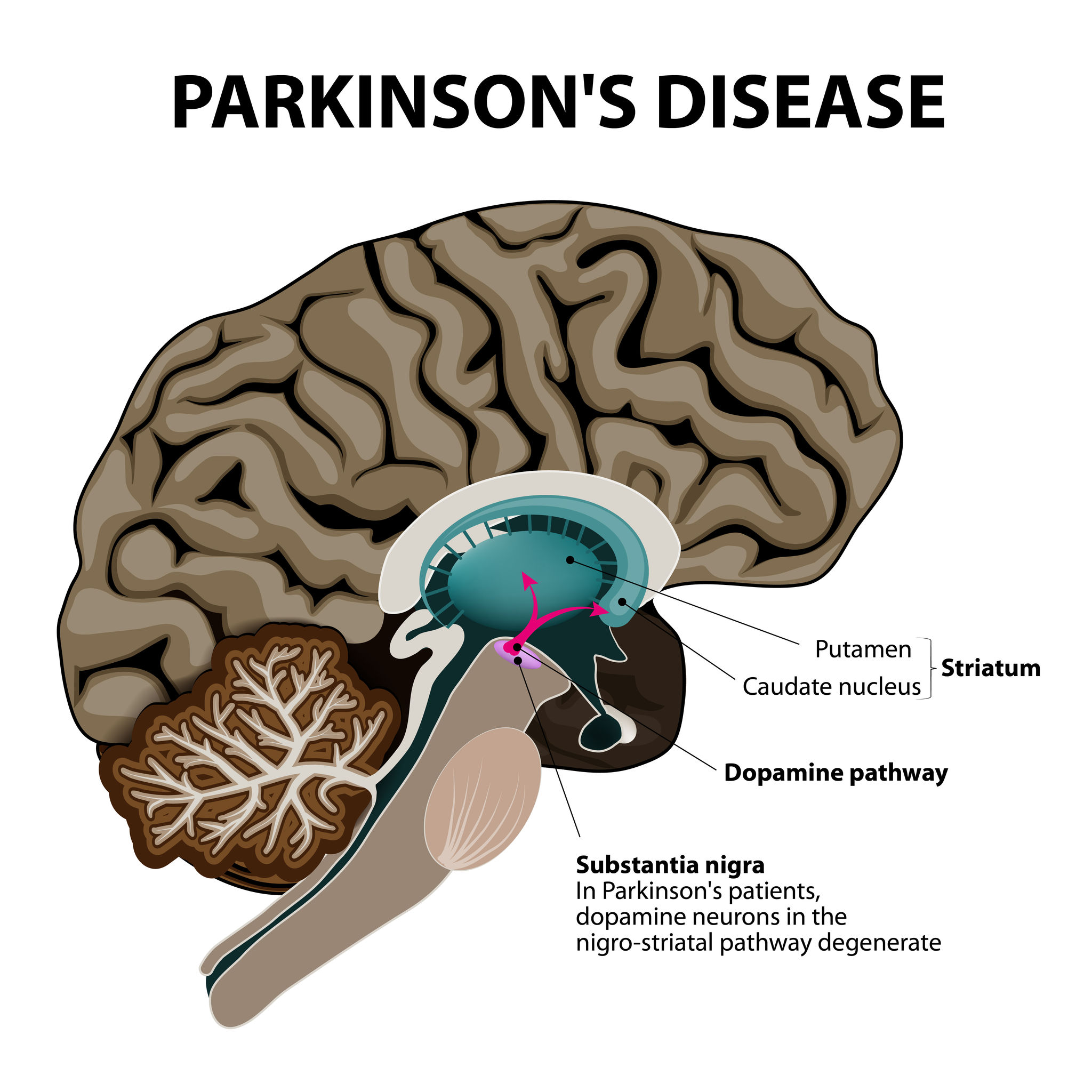
The motor symptoms of the disease are due to cell death in the substantia nigra which is located in the midbrain. This results in not enough dopamine in this area which is a critical neurotransimitter that allows nerves to communicate with each other.
What causes Parkinson’s disease?
It is not clear what causes Parkinson’s disease. The most accepted theory in the literature is that it is a combination of environmental factors and genetics (meaning is hereditary). Meaning, a number of cases of people with Parkinson’s disease were exposed to certain pesticides. Researchers have also found that people who have a family member with Parkinson’s disease are more likely to develop the disease.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease?
Symptoms vary slightly from person to person, and usually develop slowly over several years. The most notable symptoms include:
- Tremor in the hand
- Bradykinesia – slow movement
- Limb rigidity –
- Walking and balance problems
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease
In most cases, a diagnosis is based on symptoms. Doctors will typically arrive at a diagnosis by using neuroimaging to rule out all other potential differential diagnoses.
Other Posts You Might be Interested in:
Parkinson’s Disease: Managing Depression
Depression is common problem associated with Parkinson's disease (PD) and can affect all aspects of your life. In fact, it is estimated that approx. 40-50% of those diagnosed with PD experience depression. Depression is a serious mental illness that causes severe...
Product Spotlight: #1 Walker for Parkinson’s Disease
What is the best walker for Parkinson's disease (PD)? Maybe you are not there yet. Maybe you are hesitant to even approach the idea of a walker. Well, I have you covered. After nearly 20 years of working with people living with PD, I know how you might be feeling. The...
When to start Parkinson’s disease medication?
Due to the neurodegenerative nature of Parkinson's disease, there is no cure. While many medications claim to "treat" the disease, none actually reverse the effects of the disease. Parkinson's Disease Medication The main family of drugs useful for treating the motor...