8 Common Stretching Mistakes in Stroke Recovery
Why Your Stretching Might Be Making Spasticity Worse
If you’re dealing with spasticity after a neurologic injury, stretching might not be as straightforward as it seems. In fact, doing it the wrong way can increase resistance, worsen symptoms, and set your progress back.
Spasticity vs. Tightness: Know the Difference
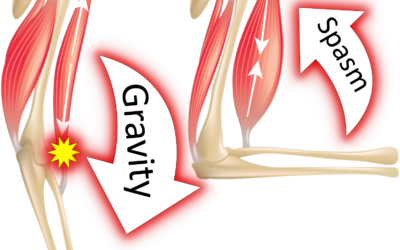
One of the most common misconceptions is treating spasticity like muscle tightness. Spasticity is an involuntary muscle contraction due to a loss of connection with parts of the brain that help to inhibit overactive movements. While a tight muscle simply needs lengthening, a spastic muscle resists lengthening and often contracts more with speed or stimulation. That’s why standard stretching techniques don’t always work.
The 8 Stretching Mistakes to Avoid
- Prolonged Holds Without Movement
Long static holds may help tight muscles but not spastic ones. Instead, incorporate slow, rhythmic movements to help desensitize the muscle. - Stretching Too Fast
Spasticity is velocity-dependent, which means the faster you stretch, the worse it gets. Go slow, always. - Only Stretching Once a Day
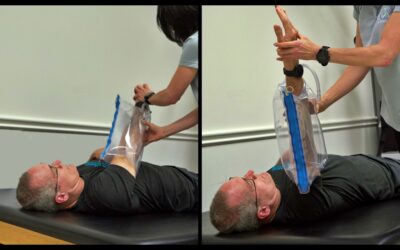
Even 30 minutes of stretching isn’t enough if the muscle contracts involuntarily the rest of the day. Wearing a properly fitted splint can help maintain gains. Most off-the-shelf splints aren’t strong enough to resist spastic contractions. Use one designed for neurologic conditions, or you can order our Rehab HQ hand brace. - Stretching in the Wrong Position
Stretching in unsupported or upright positions may trigger more resistance. Support the arm or lie down to reduce stimulation. - High-Stimulation Environments
Noisy, bright, or stressful environments increase spasticity. Do your stretching in a calm, quiet, low-stimulation space. - Lack of Active Engagement
Combine passive stretches with active-assisted or antagonist muscle activation to promote balance and relaxation. - Skipping Weight-Bearing Stretches
Weight-bearing (e.g., standing calf stretches or resting your forearm on a table) can reduce spasticity more effectively than sitting. - Engage Your Brain
Don’t mentally check out. Engaging your brain during stretching by mentally focusing on relaxing the muscle can help with inhibition and improve results over time.
Final Thoughts
Stretching spastic muscles requires more than just time and effort, it demands the right strategy. By avoiding these common mistakes and using techniques tailored for spasticity, you can reduce resistance, improve muscle control, and make your stretching routine more effective.
Consistency, proper positioning, and staying mentally engaged are key. With the right tools and guidance, you can take meaningful steps toward better mobility and recovery.
Tools to Supercharge Your Recovery
Want a comprehensive rehab plan without bouncing between therapists or feeling lost?
Our Gold Membership Program includes:
- Ad free videos and handouts
-
Full access to 350+ home rehab exercise videos
-
Monthly Q&A sessions and webinars
-
A private discussion board I check daily
👉 Learn more at Rehab HQ
📞 Or schedule a discovery call to find out if it’s right for you.
🖐 Rehab HQ Hand Brace Ordering Form
🟦 ShoulderFlex (Blue Shoulder Stretching Tool)
Articles you may be interested in
Product Spotlight: Stroke Arm Exercise for Spasticity
Spasticity and abnormal movement patterns can make it difficult to perform stroke arm exercise. The Urias air splint can be an invaluable tool to minimize involuntary arm contractions, reduce pain, prevent contractures, and make it one thousand times easier to manage...
Product Spotlight: #1 Walker for Parkinson’s Disease
What is the best walker for Parkinson's disease (PD)? Maybe you are not there yet. Maybe you are hesitant to even approach the idea of a walker. Well, I have you covered. After nearly 20 years of working with people living with PD, I know how you might be feeling. The...
When to start Parkinson’s disease medication?
Due to the neurodegenerative nature of Parkinson's disease, there is no cure. While many medications claim to "treat" the disease, none actually reverse the effects of the disease. Parkinson's Disease Medication The main family of drugs useful for treating the motor...
Best Method for Stretching Spastic Muscles
Stretching spastic muscles is critical after a stroke. Spasticity is a movement disorder that causes an involuntary muscle contraction in response to lengthening. This occurs if there has been damage to the brain or spinal cord. This can make movement retraining and...
What is spasticity?
Spasticity is an involuntary muscle contraction caused by a hyperexcitability of the reflex arc that occurs due to damage to the brain or the spinal cord. Huh?? Yeah, agreed. Ok, I get it, keep it simple. Did you ever wonder why your leg seems to spaz out for no...
Does Mirror Therapy Improve Arm Function?
Mirror therapy (MT) is one of several effective treatments used to regain arm movement after a stroke. Mirror Therapy Background MT was originally designed to treat phantom limb pain with amputees. The way it worked was that it gave the person the sensation that they...
Mental Practice Helps Movement Recovery after a Stroke
Mental practice is a way of relearning movement (motor functions) by creating an image in your mind of the body performing that movement without the body actually moving. This method of enhancing performance and/or improving a motor skill has been used for decades in...
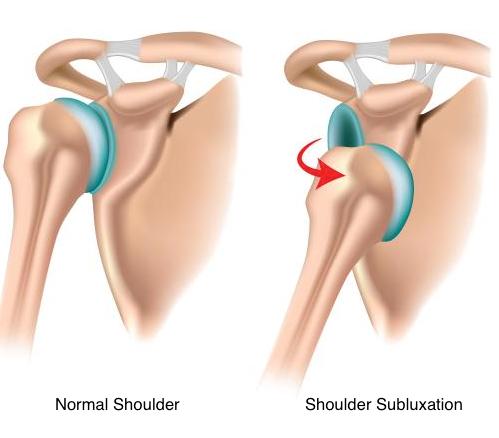
The Best Treatment for Shoulder Subluxation
A shoulder subluxation is a result of severe shoulder instability after a stroke. This can cause pain and have a negative impact on regaining active shoulder movement. What is a stroke shoulder subluxation? A shoulder subluxation is when the arm bone (humerus)...
What is Neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to form new connections (rewire) after a brain injury or a stroke. Recovery of motor (movement) function after a stroke involves relearning motor skills using this idea of neuroplasticity. Furthermore, this idea of brain...
Best Foot Drop Braces
Drop foot is when the muscles that lift the foot are not working properly. Hence, leading to the name, drop foot or foot drop. Needless, to say this can lead to difficulty walking. When I think of someone who has drop foot, my number one concern is the risk of...