Reclaim Your Stride: Fixing Abducted Gait After Stroke
Recovering from a neurological injury can affect your walking pattern, one of which is the “abducted leg walking pattern.”
In this post, we’ll cover what it is, its causes, and how to improve your walking at home. Whether you’re new to recovery or have been using an assistive device, this guide provides practical exercises to help you regain confidence and independence.
What is an Abducted Leg Walking Pattern?
An abducted leg walking pattern occurs when a person’s leg is positioned away from their body’s midline—essentially, the leg is pushed out to the side while walking.
A common sign of this pattern is the inability to keep the affected leg close to the body’s center, which can result in the leg being further out to the side than usual.
Signs of an Abducted Leg Walking Pattern:
✅ Wrist pain on the non-affected side
✅ Noticeable footstep or stomping sound on the non-affected side
✅ Use of a hemiwalker for support
Causes of the Abducted Leg Walking Pattern
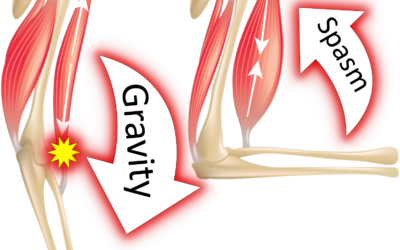
- Spasticity: This is the stiffening of muscles, making movement difficult.
- Abnormal synergy patterns: The muscles may not work together properly, causing uncoordinated movements.
- Inability to dissociate: This refers to the difficulty of moving one part of the body independently of another.
- Weakness: Lack of strength, especially in the affected leg, can make it hard to bear weight properly.
There are also some unique causes that can lead to this issue:
- Loss of orientation to midline: The brain may lose the ability to recognize the body’s center line, affecting how the legs move.
- Inability to coordinate lateral and anterior weight shifts: Shifting weight from side to side or front to back can be challenging, leading to an abducted leg position.
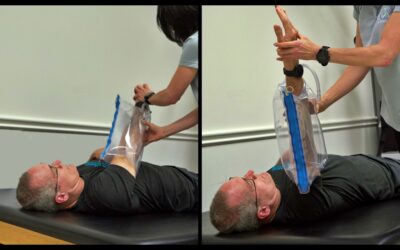
If you’re ready to work on improving your walking pattern, there are exercises you can do right at home using simple tools.
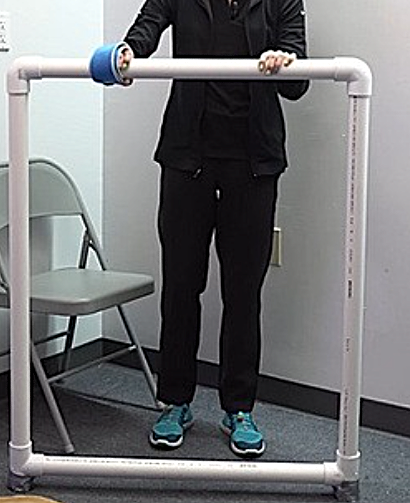
For instance, PVC pipes from a hardware store like Home Depot can be used to create a support frame. Here’s how you can get started.
Materials:
-
PVC pipes (1 and 1/2 inch thickness)
-
The pipes should be chest height and wider than shoulder-width apart
Progression Exercises:
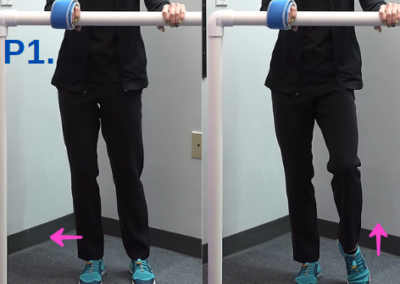
Progression 1: Weight Shifting and Heel Lifting
- Stand while holding onto anything stable or a PVC pipes for support.
- Shift your weight onto the affected leg.
- Lift the heel of the opposite foot.
- If needed, strap your hand to the pipe for extra stability
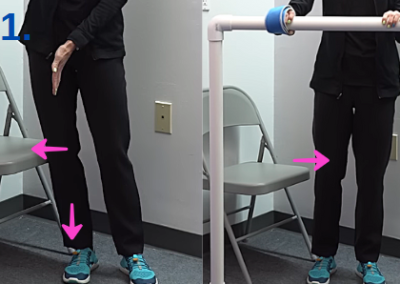
Modification for Confidence Building:
- Place your foot one fist away from a sturdy chair or object.
- Lean into the chair while keeping your belly button directly over the affected leg.
- Return to original position.
Progression 2: Sliding and Stepping with Support
- Hold onto the PVC frame for stability.
- Shift your weight onto the affected leg.
- Lift your heel.
- Slide your foot outward using a furniture slider.
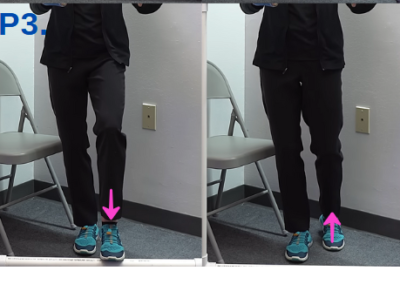
Progression 3: Step and Hold with Support
- Hold onto the PVC pipes for balance.
- Shift your weight over your foot (avoid locking your knee).
- Lift your heel.
- Step onto the front of the PVC pipe.
-
Step back down.
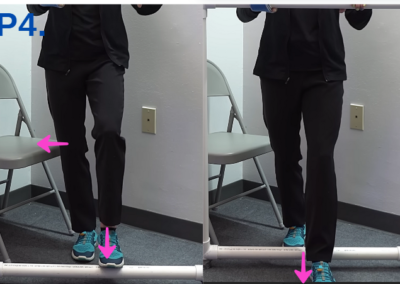
Progression 4: Incorporating Anterior Weight Shift
- Shift your weight forward.
- Step onto the PVC pipe with your affected foot.
- Step over the pipe.
- Step back to the starting position.
Exercises for Those Walking Without an Assistive Device
A. Weight Shift and Toe Control
- Sit in a chair.
- Shift your weight to the affected leg.
- Keep your big toe down (don’t let it lift).
- Step your foot across your other foot in a straight line.
- Hold the position for as long as you can.
B. Hover Exercise: step in line
- Stand with your foot slightly away from a chair.
- Step across your other foot in a straight line.
- Hover near the chair without touching it for support.
- Step back.
C: Hover Exercise – Step Across
- Position your foot slightly away from the chair.
- Shift your weight to the affected leg.
- Step across your midline with the opposite foot.
- Hover toward the chair without touching it.
- Step back to the starting position.
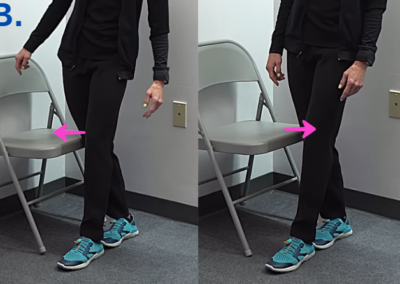
D. Stepping Strategy for Fall Prevention
How the body responds to imbalance:
1️⃣ First, we use our legs to regain balance.
2️⃣ If the imbalance is too great, we use a stepping strategy to prevent a fall.
Exercise:
- Stand with your foot positioned slightly away from a sturdy chair.
- Shift your weight and step across behind the other leg (similar to a curtsy squat).
- Step back to your original position.
Advanced Drills Using a Yoga Block
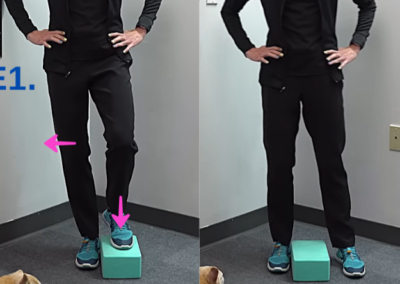
E1: Tapping the Block
- Shift your weight onto the affected leg.
- Tap the yoga block with your foot.
- Step back down.
- Progression: Flip the yoga block to a taller position and repeat.
Progression 1: Stepping Over the Block
- Stand with the affected leg next to the yoga block.
- Step onto the block.
- Step over the block.
- Step back to the starting position.
Progression 2: Flip the Block
- Stand with the affected leg next to the yoga block.
- Step onto the block.
- Step over the block.
- Step back to the starting position.
Advanced Balance & Walking Progressions:
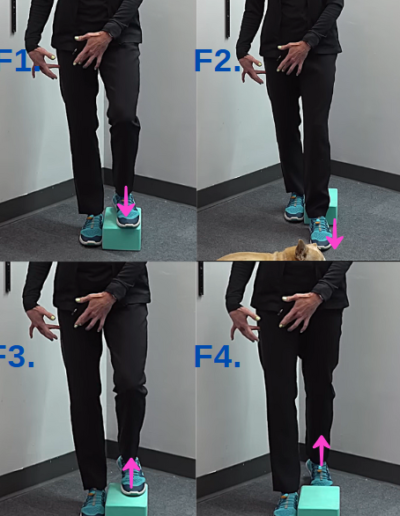
F. Step Over in Tandem
- Stand with your involved leg next to a yoga block.
- Step up onto the block with your involved leg.
- Step over the block with your other leg.
- Step back onto the block with the opposite foot.
- Return to the starting position by stepping down.
G. Tandem Walking Drill
- Stand heel-to-toe, with one foot placed directly in front of the other.
- Focus on shifting your weight laterally (side to side) and anteriorly (forward).
- Try walking forward and backward in this heel-to-toe position.
Conclusion
Abnormal gait patterns, such as an abducted leg gait, are common challenges faced by stroke survivors. By focusing on strengthening the hip abductors, engaging in consistent gait training, and utilizing assistive devices appropriately, individuals can work towards improving mobility and quality of life. It’s essential to collaborate with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan, ensuring that exercises and strategies are tailored to individual needs and progress is regularly assessed.
Consistent practice of lateral and anterior weight shifts is essential for enhancing balance and mobility. Regular engagement in these exercises builds strength and boosts confidence. Acknowledge that even the smallest steps signify meaningful progress.
Articles you might be interested in
Balance Problems After a Stroke
Balance is an even distribution of weight within a base to maintain an upright position. Balance problems are very common after a stroke. Balance is a critical part of almost all of our daily activities. Lack of balance confidence can elicit fear and anxiety. More...
Does Constraint Induced Movement Therapy Improve Arm Recovery?
Hemiplegia (weakness on one side of the body) can be a huge cause of disability following a stroke. This can make activities such as grasping, reaching, and manipulating objects difficult, if not impossible. Constraint Induced Movement Therapy has been well...
What is a muscle synergy?
In the world of neurologic movement disorders, we talk a lot about "abnormal synergy patterns". And they kind of "get a bad rap" in how they can inhibit motor (movement) recovery. But functional muscle synergies are not necessarily a bad thing. Here we are going to...
Getting up after a fall
Falling can be a scary thing. Getting up from the floor after a fall is the number one most important skill to learn. Safety Warning: Check in with your body before moving It is important to note, you should only attempt to get up if you are not injured for...
Product Spotlight: Stroke Arm Exercise for Spasticity
Spasticity and abnormal movement patterns can make it difficult to perform stroke arm exercise. The Urias air splint can be an invaluable tool to minimize involuntary arm contractions, reduce pain, prevent contractures, and make it one thousand times easier to manage...
Product Spotlight: #1 Walker for Parkinson’s Disease
What is the best walker for Parkinson's disease (PD)? Maybe you are not there yet. Maybe you are hesitant to even approach the idea of a walker. Well, I have you covered. After nearly 20 years of working with people living with PD, I know how you might be feeling. The...
When to start Parkinson’s disease medication?
Due to the neurodegenerative nature of Parkinson's disease, there is no cure. While many medications claim to "treat" the disease, none actually reverse the effects of the disease. Parkinson's Disease Medication The main family of drugs useful for treating the motor...
Best Method for Stretching Spastic Muscles
Stretching spastic muscles is critical after a stroke. Spasticity is a movement disorder that causes an involuntary muscle contraction in response to lengthening. This occurs if there has been damage to the brain or spinal cord. This can make movement retraining and...
What is spasticity?
Spasticity is an involuntary muscle contraction caused by a hyperexcitability of the reflex arc that occurs due to damage to the brain or the spinal cord. Huh?? Yeah, agreed. Ok, I get it, keep it simple. Did you ever wonder why your leg seems to spaz out for no...
Does Mirror Therapy Improve Arm Function?
Mirror therapy (MT) is one of several effective treatments used to regain arm movement after a stroke. Mirror Therapy Background MT was originally designed to treat phantom limb pain with amputees. The way it worked was that it gave the person the sensation that they...