8 Neuro Rehab Myths That Are Holding You Back (And What to Do Instead)
Debunking Common Myths About Neurologic Recovery
If you’ve ever been told that your recovery after a neurologic injury has an expiration date, or if your physical therapy has focused only on walking speed, this post is for you. Outdated beliefs in the healthcare system can hold people back from true recovery. We’re breaking down the most common myths and revealing the truth that can help you take ownership of your rehab journey.
Myth 1: Recovery Stops After 18 Months
Many patients are told there’s a point after which no new progress is possible. This is false.
The Truth: Your brain can rewire itself throughout your entire life. Neuroplasticity doesn’t stop after six months, a year, or even 18 months. Many patients make progress years after their injury, gaining new movement and independence. Supportive caregivers, repetition, and a growth mindset make this recovery possible.
Myth 2: Walking Speed is the Ultimate Goal
Many traditional therapists focus heavily on gait speed, often citing 1.4 meters per second as a benchmark.
The Truth: While walking speed has value (it relates to community mobility and fall risk), it’s not the most important measure of recovery. Overemphasis on speed can create harmful compensatory patterns, making it harder to restore movement on the affected side. The real goal should be quality of movement, not just speed.
Myth 3: “No Pain, No Gain” or “Pain means stop”
Pain advice is confusing. Some say push through it, others say avoid it entirely.
The Truth: Both extremes are misleading. Mild, tolerable discomfort is necessary to retrain your nervous system, but pushing through too much pain can increase spasticity and fear. On the other hand, avoiding all pain can stall progress. The key is finding your personal pain threshold where you can work without triggering negative emotional reactions.
Myth 4: Expensive Equipment is Required for Recovery
Robotic devices, subscriptions, and high-tech therapy tools are often marketed as essential.
The Truth: Most progress comes from intentional & repetitive practice, not gadgets. Many expensive tools end up unused in closets. In most cases, a skilled therapist and simple tools are far more valuable.
Myth 5: Assistive Devices and Braces Are Crutches
Canes, AFOs, and braces are sometimes stigmatized as signs of dependency.
The Truth: Devices like AFOs or canes are not signs of weakness. They are actually tools that support recovery, reduce spasticity, promote safer walking, and improve quality of life. The real risk comes from abandoning them too early, which can worsen gait deviations.
Tip: Avoid long-term reliance on HEMI walkers.
Myth 6: If You Can’t Do It Perfectly, Don’t Do It At All
Some therapists push for perfect movement, while others focus solely on speed.
The Truth: Waiting for perfection is counterproductive. Safe, consistent practice, imperfect or not, builds confidence, strength, and neuroplasticity. Even small mistakes help the brain learn and self-correct. Avoiding activity altogether increases sedentary time, which raises the risk of secondary health problems.
Myth 7: Recovery Only Happens in Therapy Sessions
Therapy sessions are valuable, but they are not enough on their own.
The Truth: Progress isn’t limited to the clinic. True neuroplastic change requires consistent repetition outside of therapy as well. The real breakthroughs often happen at home with daily, intentional practice. Therapists can guide you, but ownership of recovery happens in your everyday routines.
Myth 8: Recovery Means Returning to How You Were Before
Many people expect steady progress, but recovery often comes in fits and starts.
The Truth: Recovery is not always about going back to your “old normal.” It’s about creating a new normal where you can regain independence, adapt, and thrive. Even if some functions don’t return exactly as they were, you can still build meaningful strength, movement, and confidence to live fully.
Final Thoughts
Neurologic recovery is not limited by time, gadgets, or perfection. By letting go of outdated myths, you can embrace a balanced, realistic approach that supports lifelong progress. Remember: your brain is always capable of change, and with the right mindset, tools, and support, you can move forward in your recovery journey.
Articles you may be interested in
Balance Problems After a Stroke
Balance is an even distribution of weight within a base to maintain an upright position. Balance problems are very common after a stroke. Balance is a critical part of almost all of our daily activities. Lack of balance confidence can elicit fear and anxiety. More...
Does Constraint Induced Movement Therapy Improve Arm Recovery?
Hemiplegia (weakness on one side of the body) can be a huge cause of disability following a stroke. This can make activities such as grasping, reaching, and manipulating objects difficult, if not impossible. Constraint Induced Movement Therapy has been well...
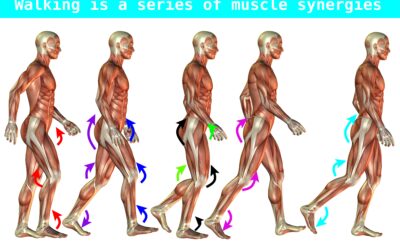
What is a muscle synergy?
In the world of neurologic movement disorders, we talk a lot about "abnormal synergy patterns". And they kind of "get a bad rap" in how they can inhibit motor (movement) recovery. But functional muscle synergies are not necessarily a bad thing. Here we are going to...
Getting up after a fall
Falling can be a scary thing. Getting up from the floor after a fall is the number one most important skill to learn. Safety Warning: Check in with your body before moving It is important to note, you should only attempt to get up if you are not injured for...
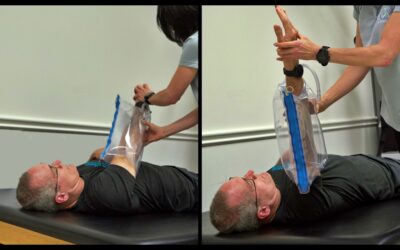
Product Spotlight: Stroke Arm Exercise for Spasticity
Spasticity and abnormal movement patterns can make it difficult to perform stroke arm exercise. The Urias air splint can be an invaluable tool to minimize involuntary arm contractions, reduce pain, prevent contractures, and make it one thousand times easier to manage...
Product Spotlight: #1 Walker for Parkinson’s Disease
What is the best walker for Parkinson's disease (PD)? Maybe you are not there yet. Maybe you are hesitant to even approach the idea of a walker. Well, I have you covered. After nearly 20 years of working with people living with PD, I know how you might be feeling. The...
When to start Parkinson’s disease medication?
Due to the neurodegenerative nature of Parkinson's disease, there is no cure. While many medications claim to "treat" the disease, none actually reverse the effects of the disease. Parkinson's Disease Medication The main family of drugs useful for treating the motor...
Best Method for Stretching Spastic Muscles
Stretching spastic muscles is critical after a stroke. Spasticity is a movement disorder that causes an involuntary muscle contraction in response to lengthening. This occurs if there has been damage to the brain or spinal cord. This can make movement retraining and...
What is spasticity?
Spasticity is an involuntary muscle contraction caused by a hyperexcitability of the reflex arc that occurs due to damage to the brain or the spinal cord. Huh?? Yeah, agreed. Ok, I get it, keep it simple. Did you ever wonder why your leg seems to spaz out for no...
Does Mirror Therapy Improve Arm Function?
Mirror therapy (MT) is one of several effective treatments used to regain arm movement after a stroke. Mirror Therapy Background MT was originally designed to treat phantom limb pain with amputees. The way it worked was that it gave the person the sensation that they...